Developing the world’s first systemic, disease-modifying treatment for RDEB
Recessive Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa (RDEB) is a devastating, rare genetic disorder affecting approximately 1–2 individuals per million. There are currently no approved systemic treatments that modify the course of the disease.
Approximately 30% of RDEB patients carry a nonsense mutation in the COL7A1 gene, leading to a premature stop codon in collagen VII, a critical adhesion protein. Read-through compounds that overcome these mutations offer the potential to restore full-length, functional collagen VII throughout the body, addressing the underlying cause of RDEB.
About RDEB
RDEB is a severe form of epidermolysis bullosa (EB), a group of rare, incurable genetic skin disorders. Patients suffer from extreme skin fragility, chronic wounds, scarring, and progressive disability. RDEB can cause life-limiting complications, including malnutrition, infections, and a high risk of aggressive skin cancers.
Current treatment is limited to supportive care, addressing symptoms rather than the root cause of the disease.
Role of Collagen VII in the skin
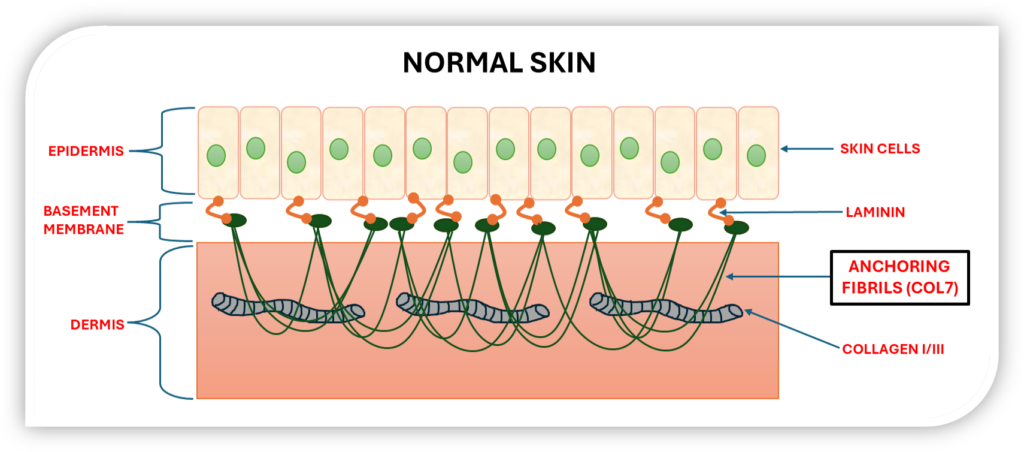
The skin is the body’s largest organ, with the epidermis tightly bound to the underlying dermis. This connection is reinforced by key proteins like Laminin and collagens I, III, and VII. Collagen VII forms anchoring fibrils that secure the epidermis to the dermis, maintaining skin strength and integrity.
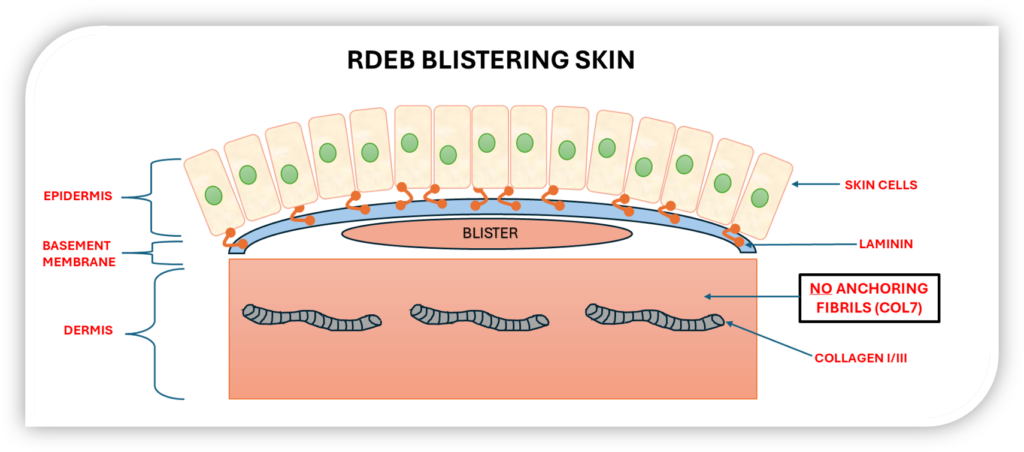
In RDEB patients with nonsense mutations in COL7A1, the absence of functional collagen VII compromises skin integrity, leading to blistering, erosions, and complications affecting the mouth, oesophagus, and other mucosal tissues.
From “Stop” to “Go” – Tackling nonsense mutations in RDEB
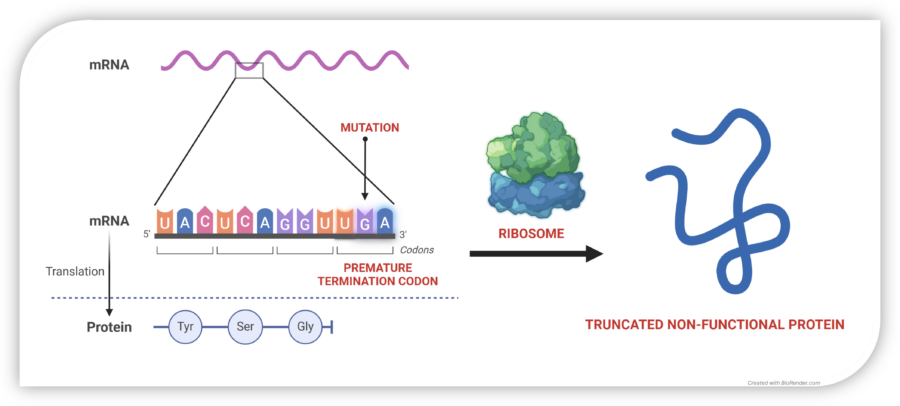
Nonsense mutations in COL7A1 cause premature stop codons, resulting in truncated, unstable, and non-functional collagen VII. This leads to skin fragility, chronic wounds, and life-limiting complications in RDEB patients.
Read-through approaches enabling ribosomes to bypass premature stop codons have been validated over decades of research but remain without an approved systemic therapy. It is estimated that as little as 2% of normal collagen VII production could modify disease progression, while levels above 20% could be effectively curative.
The Tay-Enable™ Platform
Our Tay-Enable™ platform has generated a new class of highly active, orally bioavailable, non-aminoglycoside small molecules. These compounds promote read-through of all three types of premature stop codons, restoring the production of full-length, functional proteins. We have demonstrated clinically meaningful levels of read-through in multiple RDEB patient-derived cell lines.
Our TAY-R1 program has the potential to transform care for RDEB patients with nonsense mutations and is now available for licensing to advance into clinical development.
Tay-Enable™: A Step-Change in Read-Through Therapy
Our compounds offer a differentiated approach with several key advantages over competing modalities, such as eukaryotic release factor degraders and gene therapies:
- High potency: Effective at clinically relevant concentrations.
- High efficacy: Achieving potentially curative levels of collagen VII in RDEB patient fibroblasts.
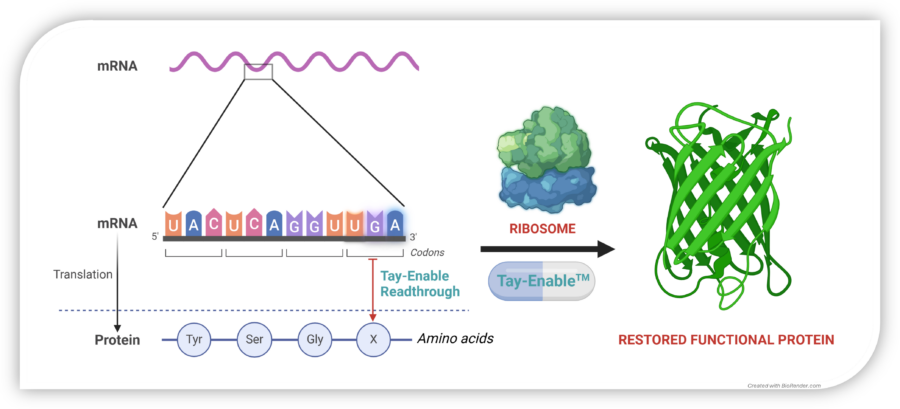
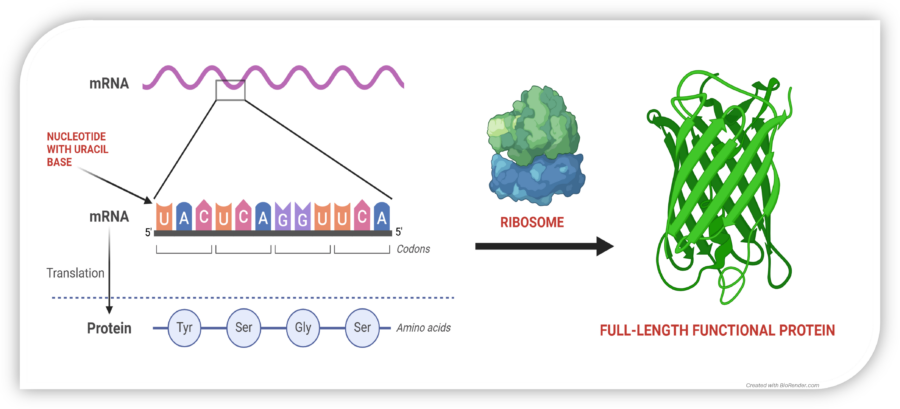
Restoring Protein Synthesis
In normal cells, mRNA is translated by the ribosome into a chain of amino acids, producing functional proteins. A nonsense mutation introduces a premature stop codon (UAG, UGA, or UAA), halting protein synthesis too early and leading to dysfunctional or absent proteins.
Tay-Enable™ compounds promote read-through at these premature stop codons, enabling the ribosome to complete translation and restore full-length, functional collagen VII production. By restoring collagen VII production, Tay-Enable™ compounds aim to deliver a disease-modifying and potentially curative treatment for RDEB and other nonsense mutation-driven diseases.
TAY-R1 is available for licensing – contact us to discuss partnering opportunities.

Developing ‘Soft’ Drugs for Targeted Delivery
While oral drugs are commercially attractive, alternative routes of administration – such as intraperitoneal, intravenous, inhaled, and topical offer the advantage of delivering therapies directly to the site of disease. At Tay Therapeutics, we specialize in developing drug candidates with the flexibility to suit multiple routes of administration. Our expertise enables the design of compounds with optimized physiochemical, pharmacokinetic, and metabolic profiles, making them suitable for oral, local, and systemic delivery. This adaptability enhances therapeutic reach and drives greater impact across our pipeline.